Production Planning Control Sap Erp Pdf Download
Diagram showing some typical ERP modules Enterprise resource planning ( ERP) is the integrated management of core business processes, often in real-time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of business- software — typically a suite of integrated —that an organization can use to collect, store, manage and interpret data from these many activities. ERP provides an integrated and continuously updated view of core business processes using common maintained by a. ERP systems track business resources—cash,, —and the status of business commitments: orders,, and. The applications that make up the system share data across various departments (manufacturing, purchasing, sales,, etc.) that provide the data.
ERP facilitates information flow between all business functions and manages connections to outside. Enterprise system software is a multibillion-dollar industry that produces components supporting a variety of business functions. IT investments have become the largest category of capital expenditure in United States-based businesses over the past [ ] decade. Though early ERP systems focused on large enterprises, smaller enterprises increasingly use ERP systems. The ERP system integrates varied organizational systems and facilitates error-free transactions and production, thereby enhancing the organization's efficiency. However, developing an ERP system differs from traditional system development. ERP systems run on a variety of and configurations, typically using a as an.
This article has been nominated to be checked for its. Discussion of this nomination can be found on the. (December 2017) () ERP Written in,, Website SAP ERP is software developed by the German company. SAP ERP incorporates the key business functions of an organization.
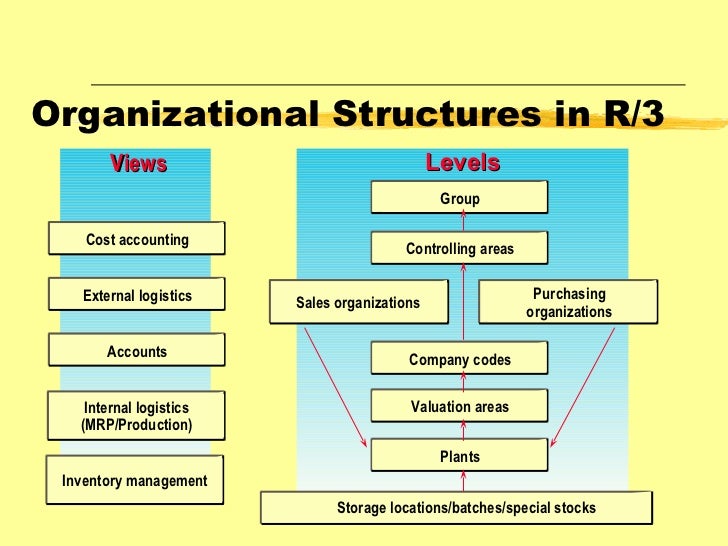
The latest version (SAP ERP 6.0) was made available in 2006. The most recent Enhancement Package (EHP8) for SAP ERP 6.0 was released in 2016. Business Processes included in SAP ERP are Operations ( &,,, Execution, and ), Financials (,, Financial Supply Chain Management), (,, e-Recruiting) and (,, and Management). Contents • • • • • • • • • • Development [ ] An ERP was built based on the former software. SAP R/3, which was officially launched on 6 July 1992, consisted of various applications on top of SAP Basis, SAP's set of programs and tools. All applications were built on top of the. Extension sets were used to deliver new features and keep the core as stable as possible.
Dec 19, 2013. Download this excerpt from Chapter 3 “Configuration Basics of Discrete Manufacturing” and Chapter 7 “Production Planning for Process Industries” from the book 'Production Planning and Control with SAP ERP' by Jawad Akhtar.

The Web Application Server contained all the capabilities of SAP Basis. A complete architecture change took place with the introduction of mySAP ERP in 2004. R/3 Enterprise was replaced with the introduction of ERP Central Component (SAP ECC). The SAP Business Warehouse, SAP Strategic Enterprise Management and Internet Transaction Server were also merged into SAP ECC, allowing users to run them under one instance. The SAP Web Application Server was wrapped into SAP, which was introduced in 2003. Architectural changes were also made to support an enterprise service architecture to transition customers to a.
The latest version, SAP ERP 6.0, was released in 2006. SAP ERP 6.0 has since then been updated through SAP enhancement packs, the most recent: SAP enhancement package 8 for SAP ERP 6.0 in 2016. Implementation [ ] SAP ERP consists of several modules, including Financial Accounting (FI), Controlling (CO), Asset Accounting (AA), Sales & Distribution (SD), Material Management (MM), Product Planning (PP), Quality Management (QM), Project System (PS), Plant Maintenance (PM), Human Resources (HR). SAP ERP collects and combines data from the separate modules to provide the company or organization with enterprise resource planning. Typical implementation phases: • Phase 1 - Project Preparation • Phase 2 - Business Blueprint • Phase 3 - Realization • Phase 4 - Final Preparation • Phase 5 - Golive Support Companies planning to implement or upgrade an SAP ERP system should pay strict attention to system integration to save their SAP ERP implementation from failure.
With system integration in place, data flows move completely and correctly among various SAP ERP components, thereby not only streamlining business processes but also eliminating or minimizing redundant data entry efforts. Analyst firm estimates that 55% to 75% of all ERP projects fail to meet their objectivesOf the top 10 barriers to a successful ERP journey, 5 can be addressed by developing and implementing a structured change management program. Deployment and maintenance costs [ ] Effectively implemented SAP ERP systems may have cost benefits: • Reduced level of inventory through improved planning and control. • Improved production efficiency which minimizes shortages and interruptions. • Reduced materials cost through improved procurement and payment protocols. • Reduced labor cost through better allocation of staff and reduced overtime.
• Increased sales revenue, driven by better managed customer relationships. • Increased gross margin percentage. • Reduced administrative costs. • Reduced regulatory compliance costs. Integration is the key in this process. 'Generally, a company's level of data integration is highest when the company uses one vendor to supply all of its modules.'
An software package has some level of integration but it depends on the expertise of the company to install the system and how the package allows the users to integrate the different modules. It is estimated that 'for a Fortune 500 company, software, hardware, and consulting costs can easily exceed $100 million (around $50 million to $500 million). Large companies can also spend $50 million to $100 million on upgrades.
Full implementation of all modules can take years,' which also adds to the end price. Midsized companies (fewer than 1,000 employees) are more likely to spend around $10 million to $20 million at most, and small companies are not likely to have the need for a fully integrated SAP ERP system unless they have the likelihood of becoming midsized and then the same data applies as would a midsized company. Independent studies have shown that deployment and maintenance costs of a SAP solution can greatly vary depending on the organization. For example, some point out that because of the rigid model imposed by SAP tools, a lot of customization code to adapt to the business process may have to be developed and maintained. Some others pointed out that a could only be obtained when there was both a sufficient number of users and sufficient frequency of use. Deploying SAP itself can also involve a lot of time and resources. SAP Transport Management System [ ] SAP Transport Management System (TMS) is a tool within systems to manage software updates, termed, on one or more connected SAP systems.
This should not be confused with SAP Transportation Management, a stand-alone module for facilitating logistics and supply chain management in the transportation of goods and materials. • Lextrait, Vincent (January 2010).. Retrieved 14 March 2010. Retrieved 2017-03-21. • Boeder, Jochen; Groene, Bernhard (2014-03-06)..
• Darmawan, Budi; Dvorak, Miroslav; Harnal, Dhruv; Murugan, Rennad; Silva, Marcos (2009). Retrieved 2017-02-15. Retrieved 2017-02-15. Retrieved 2017-02-15.
INDUSA Technical Corp. - Software Outsourcing Microsoft Partner Company Software Solutions. Fanuc Robotics Roboguide Simulation Software Download. Retrieved 2017-03-21. • ^ Monk, Ellen F.; Wagner, Brej J. Concepts in enterprise resource planning (3rd ed.). Boston: Thomson Course Technology.
Download Pokemon Shattered Dreams Beta 2. • Everett, Cath (2008-02-13).. Retrieved 2009-03-08. Around 90 percent of European SAP customers could save six- or seven quid each year by avoiding the creation of bespoke code on top of the ERP platform, an IT consultant has claimed • Vance, Ashlee (2003-03-31).. UK: The Register. Retrieved 2009-03-08. Nucleus Research.
Retrieved 2009-03-08. Customers will see benefits after lengthy implementations, but many deployments anchored down by excessive consulting costs •. USA: Fingent. Retrieved 2015-11-03. • Harvey, Tesha; Schattka, Karin (15 December 2009).. SAP Community WIKI. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
• Naveh, Moshe (24 December 2014).. SAP Community WIKI. Retrieved 2 August 2017. • Bui, Vi (11 January 2006)..
Retrieved 2 August 2017. • Oehler, Christian; Weiss, Thomas (15 December 2009).. Retrieved 2 August 2017. • Thomas, Weiss; Christian, Oehler (1 January 2009).. Retrieved 2 August 2017.
• Rau, Sabine (13 April 2016).. Retrieved 2 August 2017. • Gargeya, VB 2005, ‘Success and failure factors of adopting SAP in ERP system implementation’, Business Process Management Journal, Vol.11, No.5, pp501–516, Retrieved. • In White Paper Review, Industry Week OCT 2009, ‘ERP Best Practices: The SaaS Difference, Plex Systems, Retrieved. • Malhorta, A & Temponi, C 2010, ‘Critical decisions for ERP integration: Small business issues’, International Journal of Information Management, Vol. 30, Issue No.1, Pages 28–37,, Science Direct. External links [ ] •.